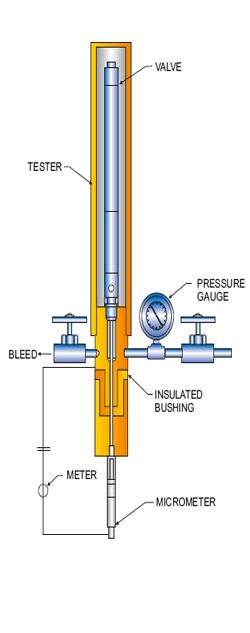
The purpose of the gas lift valve probe tester is to determine the relative “stiffness” of a gas lift valve and to determine the maximum available travel of the stem top. When gas pressure is admitted to the tester, it acts on the full area of the valve bellows to lift the stem off the seat. When this pressure increased, the stem tip lifts further off the seat. By using the valve probe tester, an accurate measure of the stem tip travel, per pressure increase, can be determined and the results tabulated and plotted.
When the pressure is plotted as the ordinate and the stem tip travel as the abscissa, a relatively straight line will be generated for the majority of the stem tip travel. The slope of this line is an indication of the “stiffness” of the valve. The numerical value of the slope is called the bellows assembly load rate (blr) and is measured in psig/inch [kpa/mm]. In this context, the “bellows assembly” includes the bellows and the system which applies a load to hold the valve stem on the seat. The higher the load rate, the “stiffer” the valve and inversely, the lower the load rate, the “softer” the valve.
If the above is done with the same valve, except that opening pressure (dome charge or spring setting) is varied, then the effect of dome charge pressure or spring setting on the bellows assembly load rate can be compared for the same type of valve when set for different opening pressures. The bellows assembly load rate is a practical value that can be used to compare different types of valves or when evaluating the same valve under different load conditions and when designing the gas lift installation.